Author
Jennifer Wessel, JD, MPH
Senior Policy Analyst and Data Privacy Officer
501-526-2244
JBWessel@achi.net
Millions of Americans have become unemployed due to the economic impact of COVID-19. In Arkansas, surging unemployment likely will result in significant changes to the state’s current patchwork quilt of health insurance coverage.
Arkansas’s unemployment rate rose to 10.2% in April — up from 4.8% in March — according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Unemployment has resulted in many workers losing employer-based health coverage, signaling potential increases in enrollment in Medicaid and the Arkansas Health Insurance Marketplace (AHIM). The State Health Access Data Assistance Center estimated 147,000 Arkansans may experience a disruption in their employer-sponsored health insurance coverage.
Income reduction from unemployment may make adults newly eligible for Arkansas Works, the state’s Medicaid expansion program that provides coverage to adults earning at or below 138% of the federal poverty level (FPL), which is $17,609 per year for an individual and $36,153 per year for a family of four.
Others who enroll in a Marketplace plan may be eligible for scaled subsidies if their annual incomes are between 139% and 400% of the FPL, or between $17,736 and $51,040 for an individual and between $36,418 and $104,800 for a family of four. As income increases, subsidies decrease. Loss of employment-based coverage qualifies individuals for a special enrollment period after the regular open enrollment period has ended.
Children in unemployed families will likely be newly eligible for ARKids First, Arkansas’s children’s insurance program. There are two kinds of coverage under the program: ARKids A, which is traditional Medicaid, and ARKids B, which is for children whose families do not qualify for traditional Medicaid but cannot afford private insurance.
There are a variety of benefits available to assist those currently out of work, some of which impact coverage options for health insurance. Unemployment benefits are generally considered income in determining eligibility for Medicaid and subsidized coverage in AHIM. 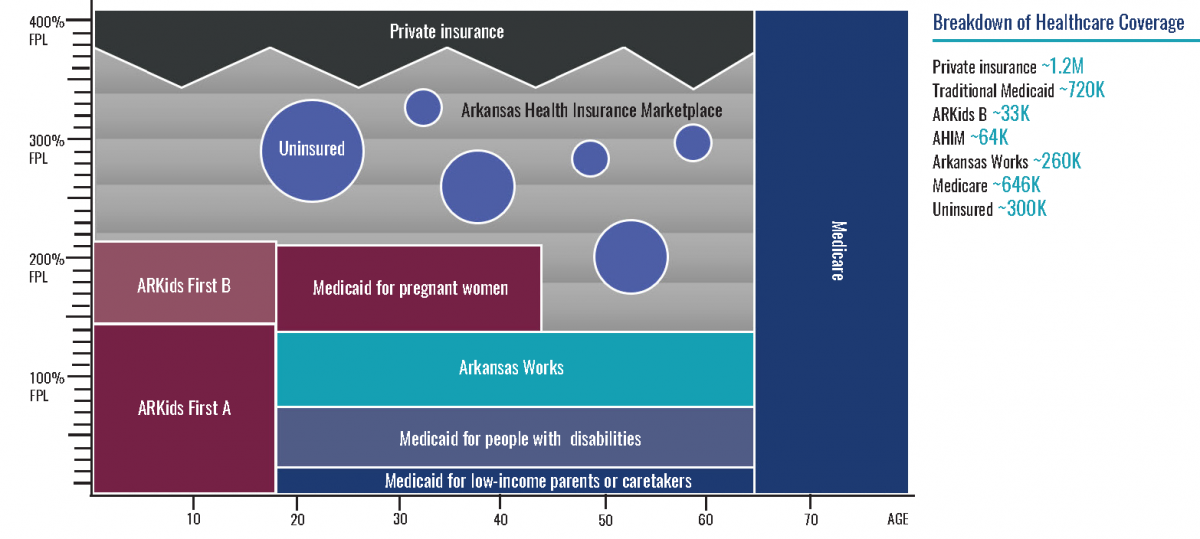
This graphic represents the patchwork of primary sources of health insurance coverage for Arkansans prior to the pandemic. The coverage sources and approximate numbers of individuals with each are:
- private insurance, 1.2 million
- traditional Medicaid, including ARKids A, 720,000
- ARKids B, 33,000
- AHIM, 64,000
- Arkansas Works, 260,000
- Medicare, 646,000
- uninsured, 300,000
Because of employment losses stemming from COVID-19 and attendant healthcare coverage loss, expect to see a shift from private insurance coverage to Medicaid, subsidized coverage through AHIM, Arkansas Works, and uninsured status.